Author: Md. Khalilur Rahman Khan, [email protected]
Former Assistant Professor of Textile Engineering, Bangladesh University of Business and Technology
Introduction: Paper yarn is a yarn formed from paper strips by employing twisting process. Due to its inherent outstanding features such as antibiotic, deodorant, moisture holding, and absorbency-quick drying properties, paper yarn has lately been highlighted as a new textile material [1].
The first recorded usage of paper_yarn was in 1638, when it was used to make shifu, a form of woven textile. Clothing woven with washi yarns is known as shifu [2]. Wa means Japanese, and shi means paper. In Japan, paper yarns have a long history. Their aristocratic quality is often compared to silk, and they have similar attributes to silk: cooling in the summer and warming in the winter.
For lace and lightweight summer scarves, washi can be knitted single strand [3]. Oji fiber co., ltd has successfully manufactured a high-quality “Paper yarn OJO+” that is both environmentally friendly and gentle on the skin at a reasonable price [4].
After many years of hibernation, the beauty and extraordinary properties of Hanji (traditional Korean paper yarn), which is one of Korea’s representative traditional cultures, have been reborn as “LohasHanjiTM” in the forms of Hanji Yarn, Hanji Fabric, and diverse Hanji items [5]. This work presents paper yarn with the goal of increasing understanding of the material.
What is Yarn?
Raw Materials: Machine-made paper yarns are primarily manufactured from Manila hemp, which are grown in Ecuador
[6]. The stem is split into sheaths and shifted for drying once the leaves have been removed. The fiber length and width are around 3.5 mm and 16–35 m, respectively, at the completion of these operations.
The cross-section varies from round to oval. Manila hemp fiber has lignin, which keeps the cellulose fibers together, and the surface is coated with flat cells; this is characteristic of Manila hemp. Three advantageous attributes of this variety of hemp are its strength, stretchability, and water-repellence [7].
The plant stalks of the Korean paper mulberry, on the other hand, are made up of bark and woody xylem [8]. Many fibers emerge after peeling off the outer bark. Paper mulberry fibers contain cellulose, hemicelluloses, lignin, and wax, which are similar to cotton fibers. Moreover, paper mulberry fibers,
unlike cotton fibers, are comprised of gum. The color of lignin-rich fibers is usually brown. This is characteristic of the paper mulberry fibers. The paper mulberry’s inner bark is made up of exceptionally strong fibers and can be utilized to make high-quality paper [9].
Waste materials such linen, nylon, acetate, cotton, polyester, and wool were blended with paper mulberry fibers to make paper [9].
The production Method of Paper Yarn
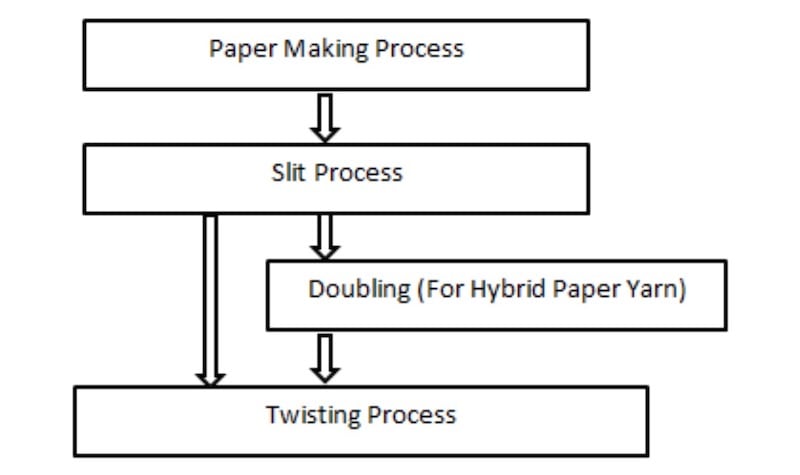
In general, there are 3 stages in the manufacturing of paper yarn: (i) paper making process to develop a paper sheet, (ii) the preparation of paper tape by cutting a paper sheet into a set width, and (iii) preparation of paper yarn by twisting the paper tape. Twist is usually in the 400-800 range, while z-twist is used for single yarn. Furthermore, a doubling and twisting procedure is employed when the paper yarn is combined with different types of yarn [1].
The strips need to be ‘condensed’ to avoid ripping of the paper during twisting [8]. Figure-1 depicts a flow chart for the production of paper_yarn. Paper yarn with a yarn count of 7-40 Ne is often made with paper tape that weighs 12-15 g/m2 and has a width of 1-6 mm [1]. Open-end spinning was also used to make yarns from a blend of cotton and paper mulberry fibers [9].
Merits of Paper Yarn
There are numerous benefits to using paper as a raw material for the production of yarn [8]. The advantages of paper for textile fibers are its breathability (excellent for humid summers), high functioning, and aesthetic [2]. Paper_yarn is lightweight, fuzz-free, and easily dyeable.
It also has superior ventilation, insulation, touch, low static electricity, and is a long-lasting material [6]. The production technique releases no toxic substances, and paper_yarn can be recycled biologically in an environmentally favorable cycle. However, it also has low softness and stretchability, and the woven fabric wrinkles easily [7].
Furthermore, demand for paper is currently declining as more people use the Internet to read newspapers, pay bills, and so on; this behavioral change has resulted in overcapacity in the pulp and paper industry, prompting the hunt for new business prospects. This difficulty might be solved with paper yarn [7].

Limitations
However, because of its low elongation and poor flexibility, it has some cut-off issues and is difficult to control tension. When paper yarn breaks frequently during the fabric manufacturing process, the woven fabric is readily knotted, and the knitted fabric is laddered and bored, causing the fabric’s outside look and physical characteristics to deteriorate significantly.
In the knitting process, needles and yarn breaking are common occurrences, and these events eventually contribute to decreased knitting efficiency. A paper yarn easily breaks in the knitting process because its surface is rough and stiff originated from its high initial modulus and low breaking strain [1].
Handling and knitting challenges with paper yarns could be avoided by treating the yarn with paraffin, oil, or some other type of moisture before knitting [7]. In the case of machine-made paper yarn, new technological advancements have eliminated these issues, resulting in a yarn that is exceedingly fine and affordable [6].
Hybrid Paper Yarn
In order to adequately improve upon the shortcomings of paper_yarn, manufacturing methods of hybrid yarn and covered yarn by merging paper yarn with a different yarn have recently been investigated and developed [7]. Paper yarn and filament yarn are doubled first, and then twisted with differing twist numbers in a twisting machine (e.g., TFO) in the production of hybrid yarn [1]. Park et al. produced combination yarn by combining paper_yarn and core spun yarn [10].
It is worth mentioning that the paper yarn was twisted with a rayon thread (54 percent paper, 46 percent viscose) to give clothes and accessories essential stability [3].
It is envisaged that the hybridization of paper yarn with synthetic filament yarn will promote the development of new clothes and textile items. A twisting procedure for converting the paper tape into a paper_yarn can be eliminated when the paper yarn is doubled and twisted with an untwisted filament yarn, and therefore this approach can make the process more inexpensive [1].
Fields of Application
Paper yarns are commonly used in high-fashion and handicraft items. Knitters and crafters employ paper_yarns. If the yarn is twisted to make it stronger, it can be used in weaving [2]. Park, for example, developed a denim fabric with paper yarns as a weft [10]. The possibilities of this material are big, including not just fashion and interior design, but also other products such as building materials [6]. Stretch fabric made using silk yarn as warp and paper_yarn as the weft is shown in figure-3.
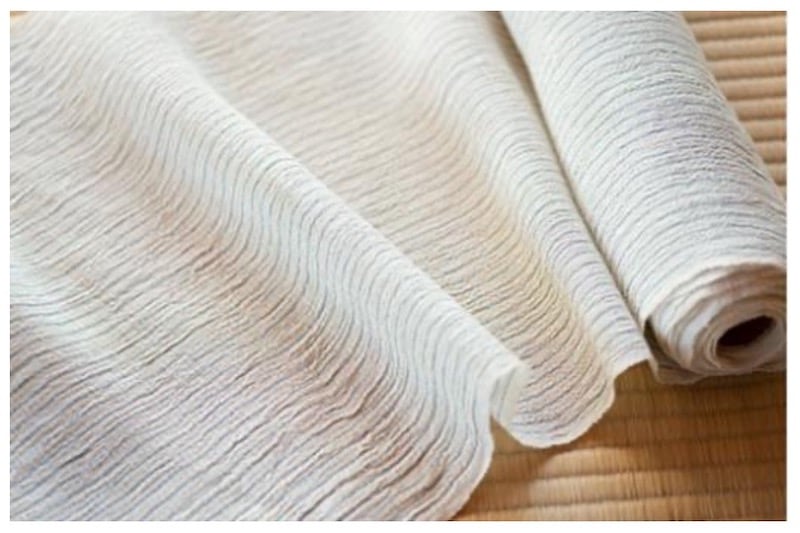

Research Opportunities
The prospect of employing paper_yarn materials for apparel, for which qualities such as handleability during knitting and weaving are vital, is an intriguing study topic. Washability, shrinkage, pilling, and tensile strength are all significant features to look for in such yarn [7].
Conclusion
This study was aimed at knowing the various aspects of paper yarn in general. Along with the short description of the manufacturing process, the advantageous features as well as the striking limitations of paper yarn are also discussed. Besides, fields of application and future research areas are also mentioned briefly in this study.
References:
1. Park, T.Y., Lee, S.G. Properties of hybrid yarn made of paper_yarn and filament yarn. Fibers Polym 18, 1208–1214 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-017-1052-6
2. https://www.swicofil.com/commerce/products/paper/272/applications
3. https://ito-yarn.com/en/yarn/ito-washi
4. http://www.ojifiber.co.jp/en/
5. http://global.hanjitex.com/28
6. http://bottega-yu.net/p_yarn.html
7. Joel Peterson, Alexandra Eckard, Josefine Hjelm & Hideaki Morikawa (2019): Mechanical- Property-Based Comparison of Paper_Yarn with Cotton, Viscose, and Polyester Yarns, Journal of Natural Fibers, DOI: 10.1080/15440478.2019.1629372
8. Jaykumar Chummun Satyadev Rosunee , (2012),”Manufacture of Folded and Twisted Paper_Yarn”, Research Journal of Textile and Apparel, Vol. 16 Iss 4 pp. 93 – 99
9. Manoon Jitjaicham, Boonsri Kusuktham, “Preparation of Paper Mulberry Fibers and Possibility of Cotton/Paper Mulberry Yarns Production”, Indian Journal of Materials Science, vol. 2016, Article ID 1498967, 6 pages, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1498967
10. Park, T.Y., Kim, MO. Manufacture and physical properties of the denim fabrics using Hanji paper_yarn as weft yarn. Fash Text 5, 26 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40691-018-0140-6
11. https://www.kppc.co.jp/en/tsunagu/vol42.html



















