Vegan leather, also known as synthetic or faux leather, has emerged as a prominent alternative to traditional animal leather. Crafted with the intention to mimic the luxurious feel and appearance of natural leather, vegan leather is gaining traction in various industries. This innovative material is composed of a range of substances, each with its unique characteristics. Understanding the key components, environmental considerations, and the ongoing dialogue surrounding vegan leather is crucial for consumers making informed choices.
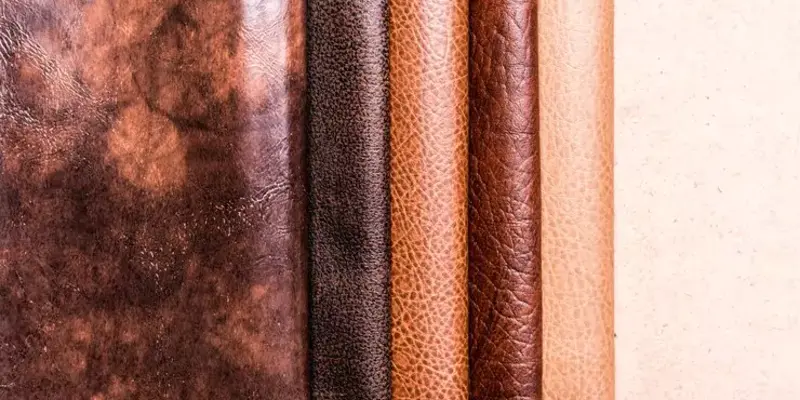
Key Characteristics and Materials of Vegan Leather:
Polyurethane (PU): Among the most prevalent materials, polyurethane is a synthetic polymer that closely resembles the texture and look of animal leather. Frequently employed in fashion items such as shoes, bags, and clothing, PU is known for its versatility.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Another synthetic plastic material, PVC, finds application in vegan leather production. Though widely used, its environmental friendliness is often questioned, making it imperative to explore alternative materials.
Microfiber: Composed of fine fibers, typically polyester or polyamide, microfiber vegan leather boasts softness, durability, and a lightweight quality. This material is favored for its comfort and eco-friendly attributes.
Recycled Materials: Eco-conscious versions of vegan leather integrate recycled materials, like polyester or other sustainable sources. This approach aims to minimize the environmental impact associated with production.
Cork Leather: Harvested from the bark of cork oak trees, cork leather is a natural and renewable resource. Widely regarded as a sustainable option, it is commonly used in accessories such as bags and wallets.
Piñatex: An innovative alternative, Piñatex is derived from pineapple leaf fibers, a byproduct of the pineapple industry. This sustainable option caters to those seeking cruelty-free alternatives with an eco-friendly touch.

Choosing Vegan Leather: Considerations and Distinctions:
Environmental Impact:
Vegan Leather: The appeal of vegan leather lies in its avoidance of animal products and the potential for a reduced environmental impact compared to traditional leather. However, the eco-friendliness varies based on materials and manufacturing processes.
Natural Leather: Traditional leather production raises environmental concerns, including deforestation and water pollution. The impact on ecosystems prompts consumers to explore alternatives.
Cruelty-Free Aspect:
Vegan Leather: A fundamental advantage is its cruelty-free nature, aligning with the ethical stance of those opposed to using animal products.
Natural Leather: Animal welfare concerns in leather production lead individuals to seek alternatives that do not involve the use of animal hides.
Durability and Maintenance:
Vegan Leather: Durability varies based on materials, but in general, vegan leather may require less maintenance than its natural counterpart and can resist water and stains.
Natural Leather: Known for its durability and the development of a unique patina, natural leather demands meticulous care and protection from moisture.
Disadvantages of Synthetic Leather:
Durability: Abrasion resistance and susceptibility to cracking can be drawbacks, affecting the longevity of synthetic leather.
Breathability: Synthetic leather may be less breathable, potentially causing discomfort in warm conditions.
Environmental Impact: Some manufacturing processes involve non-renewable resources and chemicals, contributing to environmental concerns.
Aesthetics and Feel: Texture may not fully replicate natural leather, impacting the tactile experience for some consumers.
Limited Natural Variability: Synthetic leather may lack the natural variability found in genuine leather, which some individuals appreciate.
Sensitivity to Temperature: Heat sensitivity can make synthetic leather uncomfortable in hot climates.
Cost: High-quality synthetic leather can be expensive to produce, influencing the final product’s cost.
Perception and Recognition: Despite improvements, some consumers may associate synthetic leather with lower quality compared to natural leather.
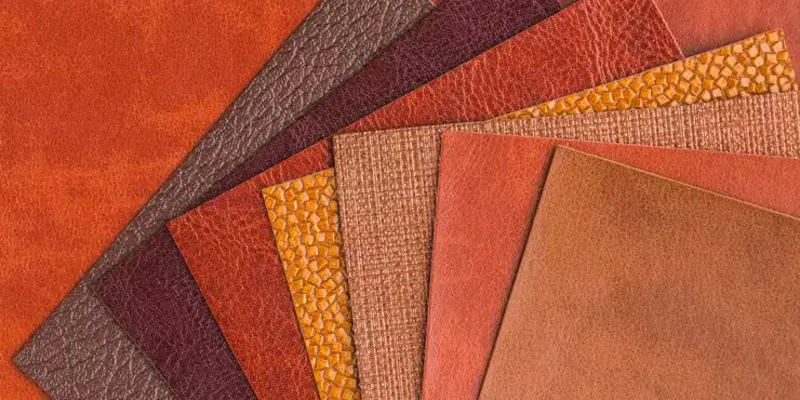

Top vegan leather producers:
There are several companies and brands that specialize in the production of vegan leather, offering cruelty-free and sustainable alternatives to traditional animal-derived leather. Here are some notable vegan leather producers.
Matt & Nat
website: www.us.mattandnat.com
Matt & Nat, founded in 1995 and based in Montreal, is certainly one of the biggest vegan leather brands in the world. They design and create modern vegan handbags using vegan leather and other vegan-approved materials, such as cork and rubber. In line with their vegan principles, all their vegan handbags are cruelty-free, and the lining is always made of 100 percent recycled bottles.
2. Stella McCartney

website: www.stellamccartney.com
Launched in 2001 by the eponymous daughter of Paul and Linda McCartney, Stella McCartney makes luxurious, cruelty-free clothing, accessories, and shoes. The sustainable brand aims to demonstrate how faux leather can push the boundaries of luxury fashion.Renowned fashion designer Stella McCartney is a prominent advocate for ethical and sustainable fashion. Her brand, Stella McCartney, produces a range of vegan leather items, including shoes, bags, and clothing.
3. Angela Roi

website: www.angelaroi.com
email: [email protected]
tel: 857.600.0771
Angela Roi stands out from the vegan leather fashion world through her commitment to ethically combining luxury and a vegan lifestyle. All of their vegan leather materials are vegan-certified and responsibly manufactured without harm to animals, making them a preferred vegan leather brand for conscious customers. They offer a price range from $55–$265, so you can find different styles and sizes to fit your budget.
4. Nupelle

website:www.foremostleather.com
email: [email protected]
tel: (886)2 2365 5958
Nupelle is a brand that prides itself on designing exclusive leather alternatives. As a PETA-certified brand, the manufacturer offers a wide variety of vegan leather. Currently, they have four different types of vegan leather. Nupelle sources raw materials such as fruit waste, pineapple waste, and recycled plastic to create vegan leather. Of these, PANEX™ is vegan leather made from waste pineapple fiber and pulps. It is partially biodegradable.
5. Desserto®

website: www.desserto.com.mx
With the purpose of creating an alternative to animal leather, Adrián López Velarde and Marte Cázarez, both hailing from Mexico, developed a vegan alternative to leather made with nopal (a cactus), which they successfully showcased last October 2019 in Milan, Italy.After two years of research and development, the creators could finally finish marketable cactus based material as an alternative to leather in July 2019. Its trade name is Desserto®, and it has competitive features compared to animal or synthetic leather, like sustainability, performance and aesthetics.
6. Malai

website: www.malai.eco
Malai is an eco-fashion manufacturer that works with local farmers to retrieve agricultural waste. These are the raw materials used for creating vegan leather. Examples include waste coconut, banana stem, hemp fiber, and coconut water.It is a user-friendly, 100% biodegradable material that lasts years when maintained the right way. Running on a small scale, Malai aims to ramp up the production of vegan leather in the days to come.
The Future of Vegan Leather:
Predicting the future of the vegan leather industry involves considering current trends, consumer preferences, technological advancements, and environmental concerns. As sustainability becomes a focal point, ongoing advancements in materials, manufacturing processes, and consumer education are anticipated. Collaborations, increased investment, and a shift towards circular economy practices may shape the trajectory of the vegan leather industry, making it more accessible, sustainable, and aligned with evolving consumer values.
In conclusion, the dynamic landscape of vegan leather reflects a conscious shift towards cruelty-free and sustainable alternatives. As the industry responds to challenges and embraces innovation, the future holds promise for an even more diverse and environmentally responsible array of vegan leather options. Consumers, armed with knowledge, can navigate this landscape, making choices that align with their values and contribute to a more sustainable and compassionate future.



















