Introduction
Air permeability testing plays a crucial role in industries such as textiles, paper, automotive, and filtration. It measures how easily air can pass through a material, which directly impacts product performance, breathability, and durability. To ensure consistent and reliable results, air permeability test standards have been established, guiding manufacturers and laboratories in conducting accurate assessments.
This article provides a detailed exploration of air permeability test standards, covering internationally recognized methods, equipment types, calculation procedures, and result interpretation. We will also discuss how air permeability test apparatus and air permeability test equipment function, along with best practices for obtaining accurate and repeatable air permeability test results.
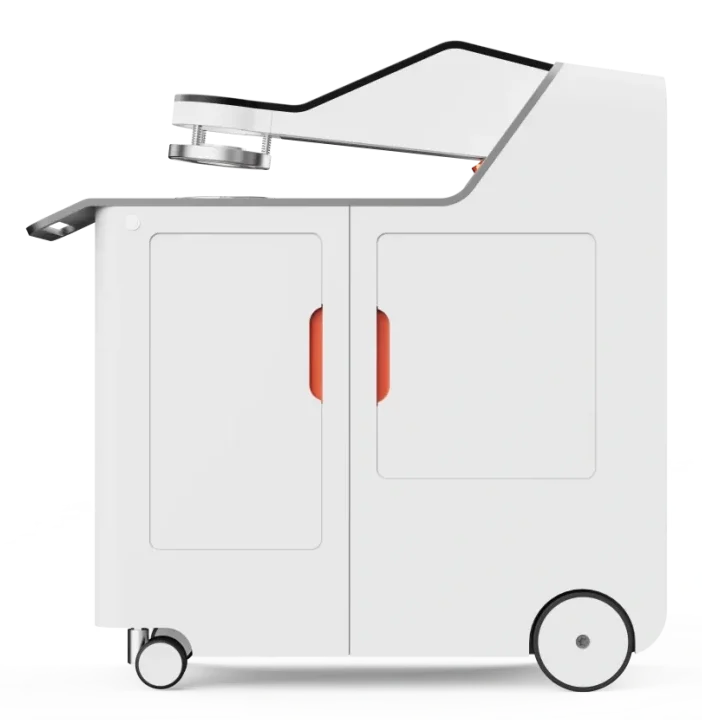

1. What Is an Air Permeability Test?
1.1 Definition and Purpose
An air permeability test measures the rate at which air passes through a material under controlled conditions. This property is critical for industries that require breathable fabrics, efficient filtration materials, and controlled airflow in packaging.
1.2 How Air Permeability Test Apparatus Works
A standard air permeability test apparatus operates by applying a controlled air pressure difference across a material sample and measuring the resulting airflow. The test setup typically includes:
- A sample holder that securely holds the material.
- A regulated air source that applies controlled pressure.
- A sensor system to measure the airflow rate.
- A digital interface for displaying and analyzing the results.
1.3 Industries That Require Air Permeability Testing
- Textiles & Apparel: Ensuring breathability in sportswear, medical garments, and outdoor clothing.
- Filtration Industry: Evaluating filter efficiency in air and water purification systems.
- Automotive & Aerospace: Testing materials used in seats, insulation, and ventilation components.
- Medical & Healthcare: Assessing the permeability of face masks, bandages, and medical fabrics.
- Paper & Packaging: Ensuring proper ventilation and durability of packaging materials.
Click here to get a quote now
2. Key Air Permeability Test Standards and Methods
2.1 International Air Permeability Test Standards
Different industries follow specific standards to ensure uniformity in testing. Some widely used standards include:
| Standard | Industry Application | Testing Conditions |
| ISO 9237 | Textiles and non-wovens | Measures airflow at a specified pressure differential |
| ASTM D737 | Textile fabrics | Determines air permeability using a standard pressure range |
| ISO 5636-5 | Paper and board materials | Measures the rate of air passage through porous papers |
| TAPPI T460 | Paper and packaging | Used in evaluating air permeability of filter papers |
| ISO 7231 | Coated fabrics | Tests permeability of waterproof and breathable materials |
2.2 Differences Between Various Air Permeability Test Standards
- ISO 9237 vs. ASTM D737: Both apply to textiles, but ISO 9237 has a wider pressure range for testing.
- ISO 5636-5 vs. TAPPI T460: Both are for paper testing, but TAPPI T460 is more commonly used in North America.
- ISO 7231: Specifically designed for coated and rubberized fabrics, unlike other standards that focus on general textiles.
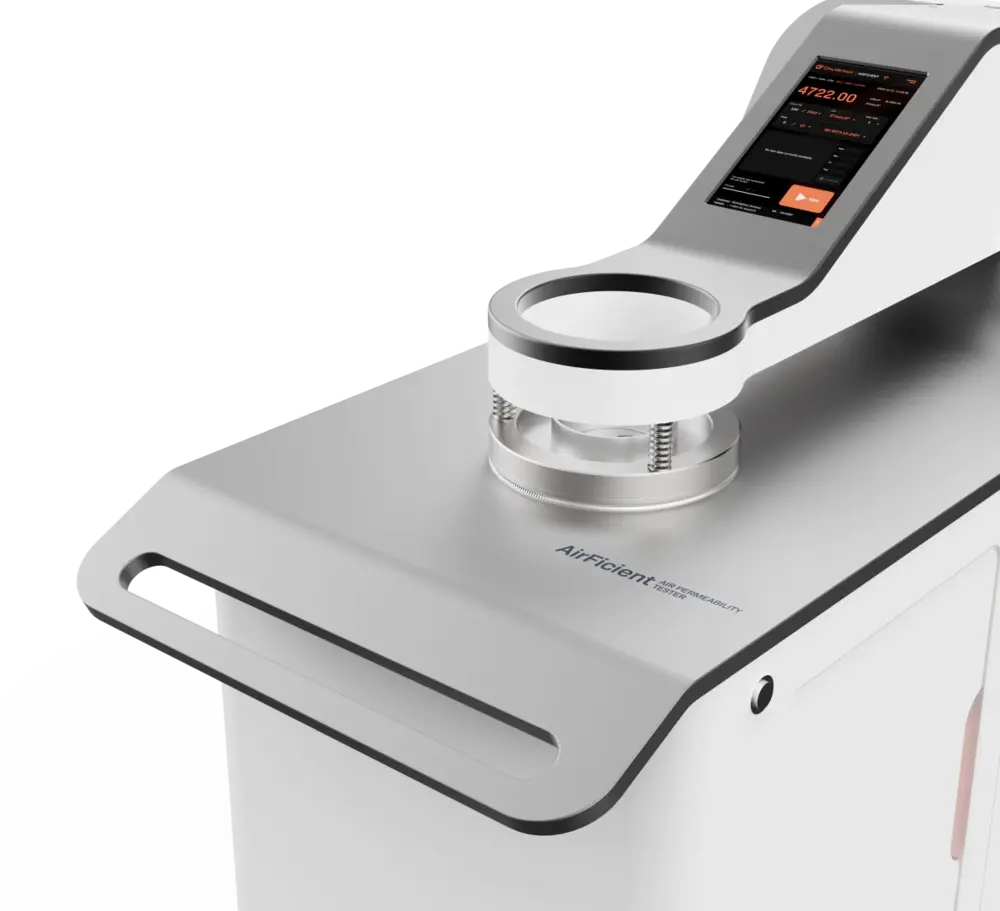

3. Air Permeability Test Apparatus: Equipment and Setup
3.1 Types of Air Permeability Test Equipment
- Manual Testers: Require operator control and are suitable for small-scale testing.
- Semi-Automatic Testers: Digital readouts and partial automation improve accuracy.
- Fully Automated Testers: Advanced models with touchscreens and data storage for industrial use.
3.2 Key Components of Air Permeability Testing Machines
- Testing Chamber: Holds the sample securely during the test.
- Air Pressure System: Applies a precise pressure difference across the material.
- Sensors and Flow Meters: Measure the rate of air passing through the sample.
- Data Processing System: Converts raw data into standardized results.
4. Air Permeability Test Procedure: Step-by-Step Guide
4.1 Sample Preparation and Environmental Factors
Cut the sample to the required size as per the test standard.
Ensure no folds, creases, or distortions that may affect the result.
Maintain controlled environmental conditions (temperature and humidity).
4.2 Conducting the Test
Place the sample in the air permeability test apparatus.
Set the required pressure difference according to the standard.
Start the test and allow the air to pass through the material.
The system records the airflow and calculates permeability.
4.3 Air Permeability Calculation Methods
The general formula for air permeability calculation is:
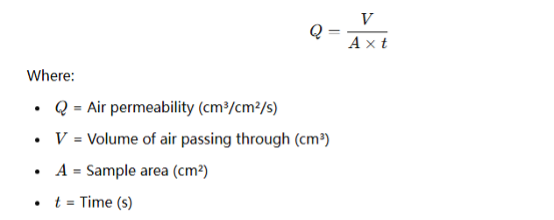
Example: If 500 cm³ of air passes through a 20 cm² fabric sample in 10 seconds, the permeability is:
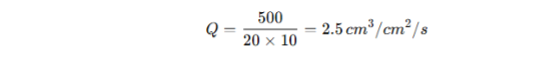
5. Understanding Air Permeability Test Results
5.1 Interpreting the Results
Higher permeability: Indicates a more breathable material (e.g., sportswear, face masks).
Lower permeability: Indicates a tighter, less porous fabric (e.g., waterproof jackets, protective clothing).
5.2 Factors Influencing Test Results
Fabric Structure: Open-weave fabrics have higher permeability than tightly woven fabrics.
Material Thickness: Thicker materials often reduce air permeability.
External Conditions: Humidity and temperature can slightly alter results.

6. Applications of Air Permeability Testing in Different Industries
6.1 Textile Industry
Determines the comfort level of clothing.
Ensures proper ventilation in industrial work wear.
6.2 Automotive and Aerospace Industry
Helps in selecting breathable seat covers.
Used in filtration material testing for vehicle air circulation.
6.3 Filtration Industry
Essential for ensuring efficiency in air and liquid filtration systems.
7. Choosing the Right Air Permeability Test Equipment
7.1 Factors to Consider
Measurement Accuracy: Important for industries requiring strict quality control.
Standard Compliance: Ensure it meets ASTM, ISO, or TAPPI standards.
Automation Level: Fully automated systems improve efficiency and reduce operator error.
7.2 Cost Considerations
Entry-Level Models: $2,000–$5,000 for basic manual testers.
Mid-Range Models: $5,000–$15,000 for digital testers with automation features.
High-End Models: $15,000–$50,000+ for fully automated systems.
8. Common Questions About Air Permeability Test Standards
Which air permeability test standard is best for textiles?
ISO 9237 and ASTM D737 are widely used for textile testing.
How often should air permeability test equipment be calibrated?
Most manufacturers recommend annual calibration for accuracy.
What factors affect air permeability test results?
Material structure, thickness, and environmental conditions.
Conclusion
Air permeability testing ensures that materials meet performance requirements across various industries. By following recognized air permeability test standards and using the right air permeability test apparatus, manufacturers can ensure consistent and reliable air permeability test results.






