The Japanese archipelago, also known as Nihon rettō in Japanese, is a country in the Pacific Ocean in Northeast Asia. It is one of the world’s major economic powers and has the third-largest GDP after the United States and China.
Japan is a wholly water-surrounded country that shares water borders with China, South Korea, North Korea, and Russia. This country’s territory was reduced to its current size of 387,000 square kilometers after the end of World War II because it lost all of its territories across the oceans, including Korea, which at the time made up 45.5% of the whole country.
With 128 million citizens, Japan is the tenth-most populated country in the world and a constitutional monarchy. With a population of over 37 million, Tokyo, as the capital of Japan, is one of the world’s biggest and most pricey capitals.
Japan saw substantial economic growth under American occupation thanks to a sustained industrial development program, becoming one of the world’s largest economies and the second-largest industrial power.
Japan has a very long history in the textile industry, which was regarded as the country’s principal industry and the cornerstone of its economy up to the start of World War II.
The United Nations states that one factor used to gauge each country’s level of social well-being is the number of fibers used per person in various products. With a per capita consumption of more than 30 kg, the United States leads the world in this regard. Japan, Canada, Australia, and Western European countries follow, with consumption ranging from 20 to 30 kg each. Naturally, it should be highlighted that developing countries fall within the range of the 10-kilogram-per-person global average.

The Japanese have a long and successful history in the textile industry, which has historically been one of this country’s most significant industrial segments. Most of the world’s modern industrial behemoths, like Toyota, began by leaning on the textile sector to fuel their industrial growth and unique innovations.
Japan consistently ranks among the world’s top 5 exporters of textiles, and Japanese businesses are very influential across various textile-related fields.
Japan is quite strong in textile machinery, notably clothing, sewing, embroidery machines, warp, and weft looms with extremely high speeds and knitting machines.
The following names can be cited as key players in Japan’s textile machinery industry:
- Toyota Textile Machinery
- TMT Textile Machinery
- Murata Spinning Machinery
- Shima Seiki Flat Knitting Technologies
- www.kanaijuyo.co.jp/
- Tsudakoma Textile Machinery

As was already mentioned, Japan is a significant producer of apparel and embroidery machines. There are 34 members of the Japan Sewing Machinery Manufacturers Association, all of which are well-known and seasoned names in the sector.
The most significant Japanese manufacturers of apparel and embroidery machines are the following names:
| Company Name:Barudan Co., Ltd. Address:20, Tsukakoshi, Jyosuiji, Ichinomiya-shi, Aichi 491-0004, Japan TEL:+81-586-76-6161 FAX:+81-586-76-6165 Category: Industrial Sewing Machine Products: Computerized Embroidery Machines, Computerized Monogram Machines, Computerized Punching Machines, Computerized Chain Stitch Embroidery Machines, Computerized Full-automatic Towel Hemming Machine |
 |
| Company Name: Brother Industries, Ltd. Address:15-1, Naeshiro-cho, Mizuho-ku, Nagoya-shi, Aichi 467-8651, Japan TEL:+81-52-824-2511 Category: Household Sewing Machine, Industrial Sewing Machine Products: Lock Stitch Sewing Machine, Special Lock Stitch Sewing Machine, Eyelet Buttonhole Sewing Machine, Programmable Electronic Pattern Sewing Machine, Overedge Sewing Machine, 1 Head Embroidery Machine |
 |
| Company Name: Happy Japan Inc. Address:3-3515, Tachiyagawa, Yamagata-shi, Yamagata 990-2251, Japan TEL:+81-23-686-2272 FAX:+81-23-686-2243 Category: Household Sewing Machine, Industrial Sewing Machine Products: Multiple Head Electronic Embroidery Machines, Household Sewing Machines, Household Overlock Stitch Machines, etc. |
 |
| Company Name: Hashima Co., Ltd. Address:7-6, Ryoga, Gifu-shi, Gifu 500-8241, Japan TEL:+81-58-245-4501 FAX:+81-58-240-5775 Category: Industrial Sewing Machine, Sewing-related Machine Products: Quilting Machines, Tape Cutter, Fusing Press Machines, Heat-transfer Press, Steam-iron |
 |
| Company Name: Hirose Mfg. Co., Ltd. Address:4-5-12, Tsukuda, Nishiyodagawa-ku, Osaka-shi, Osaka 555-0001, Japan TEL:+81-6-6476-3900 FAX:+81-6-6476-3902 Category: Sewing Machine Parts Products: Rotary Hook, Shuttle, Looper, Bobbin Case and Cap for Industrial Sewing Machine, Rotary Hook for Household Sewing Machine |
|
| Company Name:ITSUMI CO., LTD. Address:11865, Hara-mura, Suwa-gun, Nagano, 391-0107, Japan TEL:+81-266-79-2331 FAX:+81-266-79-2721 Category: Sewing-related Machine Products: Sublimation Heat Transfer Press Machine, Finishing Press Machine, Sponging Machine, etc. |
 |
| Company Name: JANOME Corporation Address:1463, Hazama-machi, Hachioji-shi, Tokyo 193-0941, Japan TEL:+81-42-661-3071 FAX:+81-42-661-3072 Category: Household Sewing Machine Products: Household Sewing Machines, Industrial Products |
 |
| Company Name: Kawakami Co., Ltd. Address:2918-8, Nagase, Mobira, Kasaoka-shi, Okayama 714-0062, Japan TEL:+81-865-66-3711 FAX:+81-865-66-3715 Category: Sewing-related Machine Products: CAD/CAM/Spreading Machines, Spreading Table, Cloth Inspecting Machines, etc. |
|
| Company Name: Kinoshita Precision Industrial Co., Ltd. Address:201, Marushin-cho, Kita-ku, Nagoya-shi, Aichi 462-0063, Japan TEL:+81-52-902-3331 FAX:+81-52-901-2757 Category: Sewing Machine Parts Products: Industrial Sewing Machine Parts |
 |
| Company Name: Morimoto Mfg. Co., Ltd. Address:180, Suna, Shijonawate-shi, Osaka 575-0001, Japan TEL:+81-72-878-1177 FAX:+81-72-879-2155 Category: Industrial Sewing Machine Products:Double Chain Stitch Machines, Blind Stitch Machines |
 |
| Company Name: Naomoto Corporation Address:19-8, Ishigatsuji-cho, Tennoji-ku, Osaka-shi, Osaka 543-0031, Japan TEL:+81-6-6775-2500 Category: Sewing-related Machine Products: Pressing Equipment and Machine, Irons, Ironing Boards and Vacuuming Boards, Boilers |
 |
| Company Name: Nishi Mfg. Co., Ltd. Address:2-11-10, Higashiuradate, Sanjyo-shi, Niigata 955-0081, Japan TEL:+81-256-32-1625 Category: Sewing Machine Parts Products: Feed Dog, Presser Foot, Throat Plate, All Kinds Knives, Laser Cutting, Sewing Machine Parts |
 |
| Company Name: Pegasus Sewing Machine Mfg. Co., Ltd. Address:5-7-2, Sagisu, Fukushima-ku, Osaka-shi, Osaka 553-0002, Japan TEL:+81-6-6451-1351 Category: Industrial Sewing Machine Products: Overlock Stitch and Safety Stitch Machine, Interlock Stitch Machine, Process Control Equipment and Systems, etc. |
 |
| Company Name: Seiko Sewing Machine Co., Ltd. Address:2-13-6, Sakae-cho, Funabashi-shi, Chiba 273-0018, Japan TEL:+81-47-420-3151 Category: Industrial Sewing Machine Products: Lock Stitch, Special Lock Stitch, Chain Stitch and Special Chain Stitch Machines, Heavy Duty Industrial Sewing Machines for Heavy Material, Sofa, Shoes, Auto-interior, etc. |
 |
| Company Name: Suzutami Precision Industry Co., Ltd. Address:1411, Takemori, Teradomari-machi, Santo-gun, Niigata 959-0161, Japan TEL:+81-256-97-2145 FAX:+81-256-98-2148 Category: Sewing Machine Parts Products: Threadcutter & Various Knife, Hot & Cold Forging Parts, Every Kind Parts for Industrial Sewing Machine |
 |
| Company Name: TISM Co., Ltd. Address:1800, Ushiyama-cho, Kasugai-shi, Aichi 486-0901, Japan TEL:+81-568-33-1161 FAX:+81-568-33-1191 Category: Industrial Sewing Machine Products: Multiple Head Electric Embroidery Machines |
 |
| Company Name: Yamato Sewing Machine Mfg. Co., Ltd. Address:4-4-12, Nishi-Tenma, Kita-ku, Osaka-shi, Osaka 530-0047, Japan TEL:+81-6-6364-5316 FAX:+81-6-6364-1307 Category: Industrial Sewing Machine Products:Overlock Stitch, Safety Stitch, Interlock Stitch, Chain Stitch and Special Chain Stitch Machines, Pocket Welting Machines, CAD |
 |
| Company Name: Yuho Sewing Machine Co., Ltd. Address:5-3-1, Biwajima, Nishi-ku, Nagoya-shi, Aichi 451-0053, Japan TEL:+81-52-522-6276 FAX:+81-52-531-9270 Category: Industrial Sewing Machine Products: Automated Sewing Machines for Men’s and Women’s Shirts, Blue jeans, Working Clothes and Interiors |
 |
| Company Name:Asahi Garment Machinery Co., Ltd. Address:2-8-30, Tatsuminaka, Ikuno-ku, Osaka-shi, Osaka 544-0013, Japan TEL:+81-6-6751-6488 FAX:+81-6-6751-6477 Category:Sewing-related Machine Products:Shrinking Machine, Fusing Machine, Press Machine, etc. |
|
| Company Name:TORAY Advanced Computer Solution INC. Address:4F, Isomura Bldg., 1-1-3, Toranomon, Minato-ku, Tokyo 105-0001, Japan TEL:+81-3-6327-7000 FAX:+81-3-6327-7009 Category: Sewing-related Machine Products: ApparelCADsystem |
 |
| Company Name:SHIMA SEIKI MFG., LTD. Address:85, Sakata, Wakayama-Shi, Wakayama 641-8511, Japan TEL:+81-73-471-0511 FAX:+81-73-474-8267 Category:Sewing-related Machine Products: Computerized flat knitting machines, Design system, Automatic fabric cutting machines |
 |
| Company Name: JUKI TECHNO SOLUTIONS CORPORATION Address:2039-1, Shimoi, Shimoi-cho, Owariasahi-shi, Aichi 488-0052, Japan, TEL:+81-561-56-1082 FAX:+81-561-56-0830 Category: Industrial Sewing Machine Products: Lock Stitch, Bartacking machine, Computer-controlled cycle machine, Overlock/safety stitch machine, Buttonholing machine |
 |
According to data, more than 28% of the textile machinery required by China is imported from Japan, making China the country where Japanese textile machinery is exported the most.
Following China are Pakistan, Indonesia, Bangladesh, and India, which import roughly 15% of their textile machinery from Japan. Southeast and South Asian countries should be regarded as the primary target markets for Japanese textile machinery companies.
Japan Chemical Fibers Industry
Many well-known brands worldwide buy these fibers from Japanese companies, which are global leaders in creating synthetic fibers. The Japanese are also particularly adept at fusing science, technology, the textile industry, and research and development. Japanese businesses have been heavily involved in developing synthetic fibers over the past few years, and they continue to discover new, unique applications across various industries.
Findings from an analysis of the consumption of various fibers in the three major sectors of the Japanese textile industry—apparel, home textiles, and industrial textiles—show that, despite a 20-year decline in the volume of apparel textile production in Japan, this index has remained consistent in the textile industry.
Among the top 18 Japanese businesses involved in the production of synthetic fibers, the following 18 can be named:
- TEIJIN LIMITED
- TORAY INDUSTRIES,INC.
- KURARAY CO.,LTD.
- TOYOBO CO.,LTD.
- ASAHI KASEI CORPORATION
- UNITIKA LTD.
- MITSUBISHI CHEMICAL CORPORATION
- FUJIBO HOLDINGS,INC.
- NITTO BOSEKI CO.,LTD.
- SEIREN CO.,LTD.
- DAIWABO CO.,LTD.
- KANEKA CORPORATION
- NITIVY CO.,LTD.
- NIPPON ESTER CO.,LTD.
- TAI-RAY CO.,LTD.
- KUREHA CORPORATION
- OSAKA GAS CEHMICALS CO., LTD.
- NIPPON GRAPHITE FIBER CORPORATION
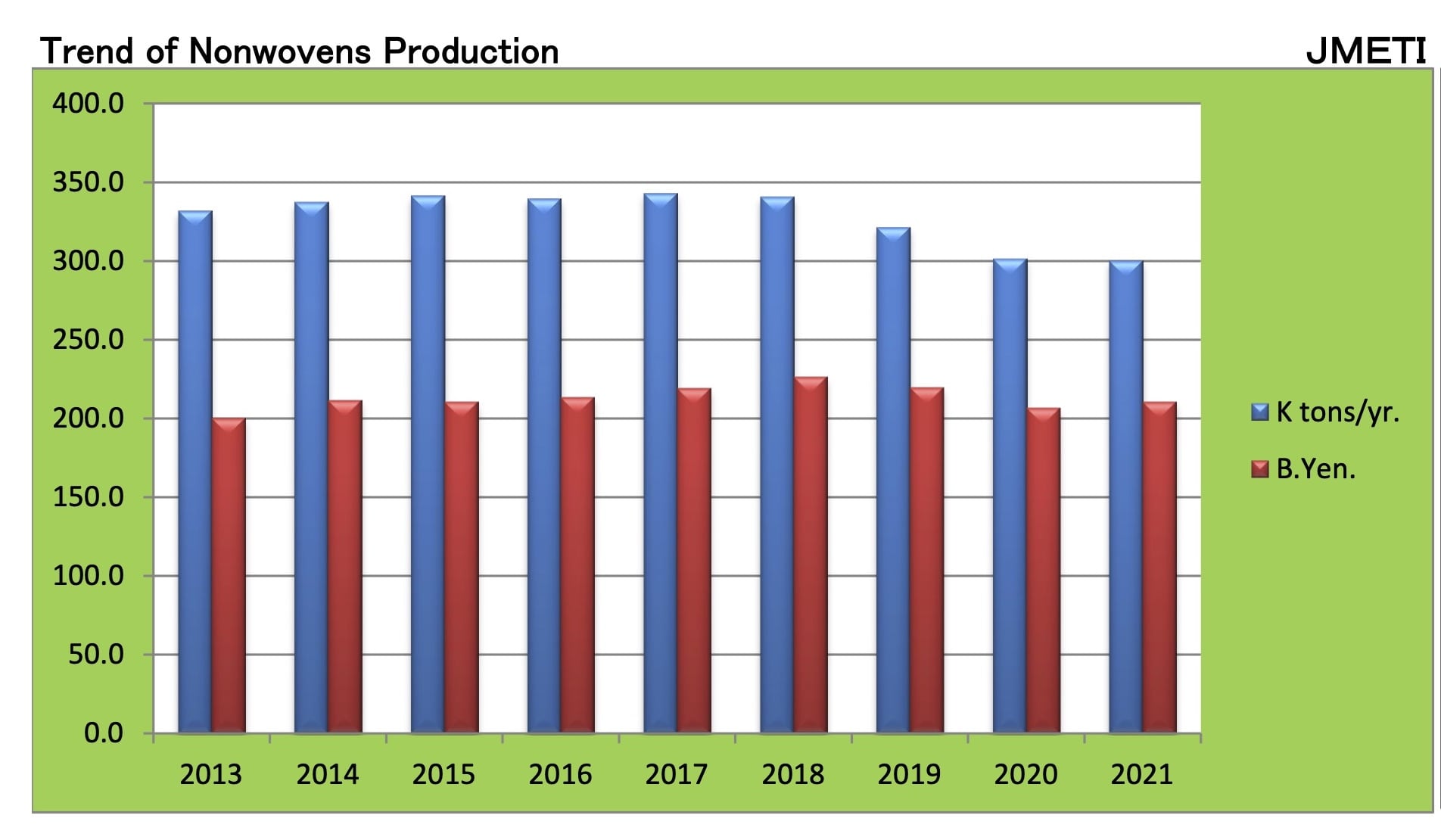
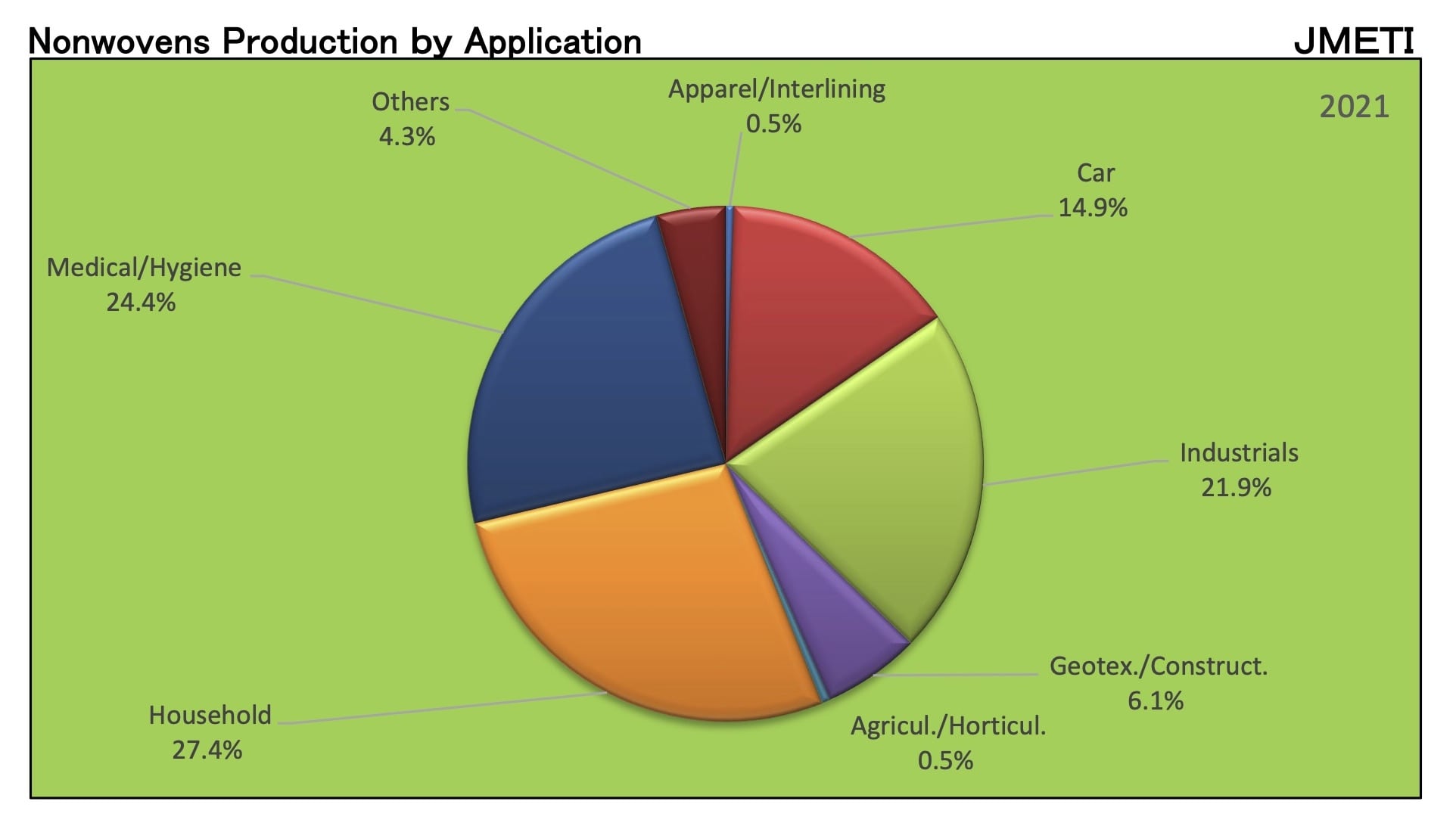
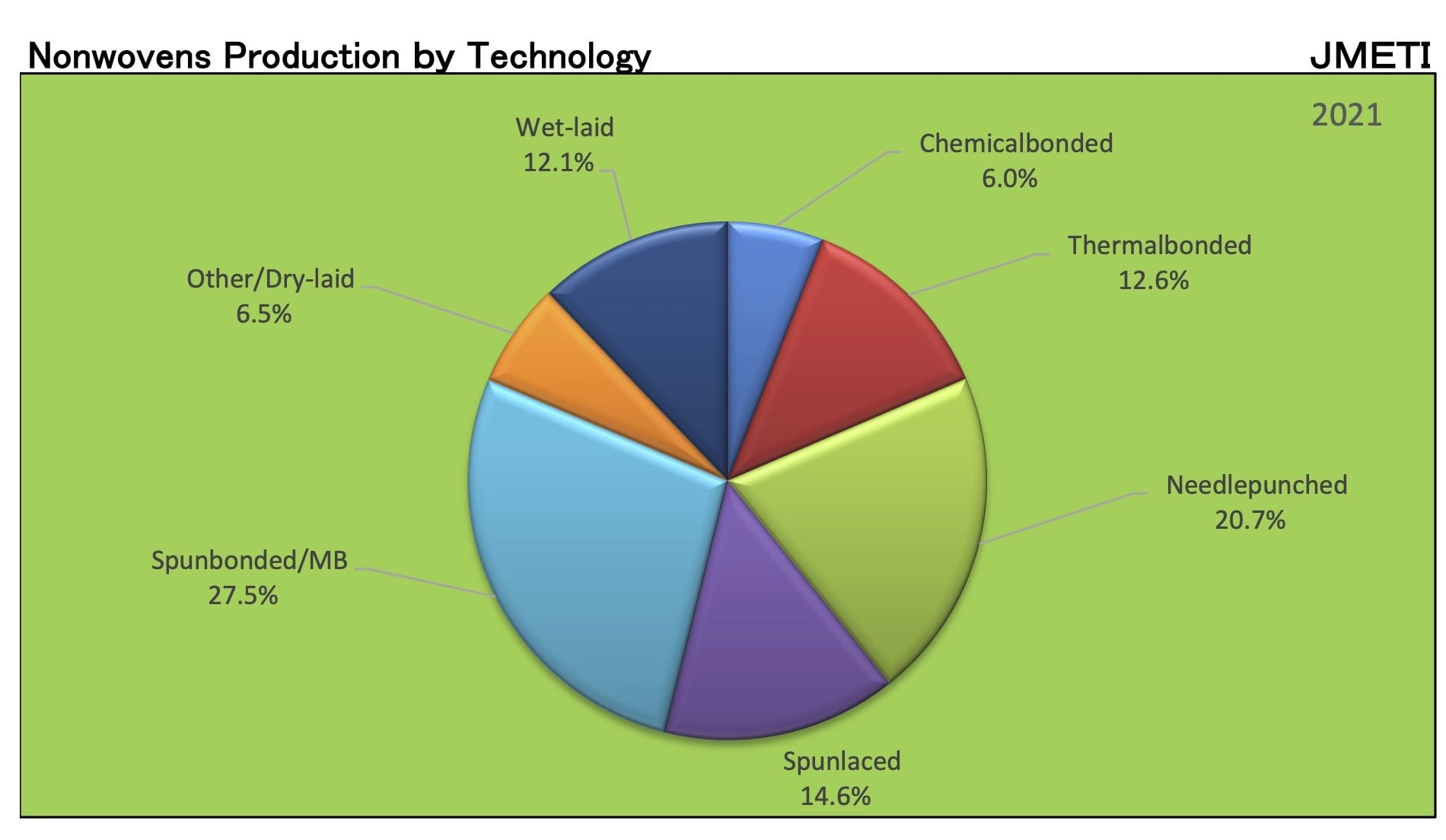
Solid position of Japan Nonwoven Industry
According to statistical studies, nonwoven fabric production increases significantly each year in China and India. But in the case of Japan, this number is essentially constant and stays within the region of 300,000 tons annually.
The existence of many nonwoven fabric production techniques in Japan is crucial in this area. Each of these approaches has approximately equal relevance in developed nations, as evidenced by the existence of these groups, which is equivalent to the present rate in Western European countries.
Naturally, this does not imply that major Japanese corporations have not altered their output but rather that they continually upgrade and replace their equipment to keep up with the needs of Japan’s cutting-edge society. To avoid higher production costs in Japan and be closer to more recent consumer markets with significant growth potential, the company transfers its brand-new investment opportunities or older machinery to neighboring Asian countries such as Korea, Taiwan, China, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand.
Non-Woven Fabrics in the Automotive Sector
The consumption of non-woven textiles in this industry sector has been impacted recently by a decline in the Japanese auto industry’s export volume. Sun Chemicals, Otsuka, Nishikawa Rose, Dainik, JVC, and Freudenberg are the most significant Japanese businesses currently operating in this market. All of these companies are searching for new markets for their products.
Non-Woven Fabrics in the Sanitary Industry
The most significant participant in this market is Unicharm Company, which recently made a name for itself as the biggest manufacturer of non-woven sanitary fabrics, including diapers and hygienic napkins, by acquiring all the shares of Miramar Company. This corporation has manufacturing facilities not just in Japan but also in several other Asian nations.
Needling Non-Woven Fabrics
The manufacturing of felts used in the paper industry in Japan is one of the major markets for such fabrics. Recently, Nippon Felt greatly expanded the range of items it can supply in this industry by introducing a new and well-equipped German production line. Nishikawa, Kurari, Torai, Unitika, Kurashiki, and Ambik are different businesses involved in this industry. Each of these companies can supply different non-woven fabric varieties for various products.
Japanese Textiles Associations
The textile business in Japan is highly specialized, and each area is managed and governed independently. The following can be listed as some of the most significant Japanese Textile Machinery Associations (JTMA):
The most renowned Japanese textile machinery manufacturers’ backgrounds
Toyota Corporation
The founder of this company, Mr. Sakichi Toyoda (Birth: 1867 – Died: 1930), was the son of a meager carpenter and began his enterprise in 1890 by producing wooden looms. He succeeded in creating the first metal power loom with an engine in 1896.
His work in this area shifted into a new era after the creation of the first circular Loom in 1906. Then, in 1926, he started a revolution in manufacturing these machines by creating the first G-type automatic warp and weft loom, with the capacity of non-stop shuttle-change movement.
As a result, the loom speed of this equipment is more than 20 times that of comparable machines. This device was chosen as the 16th sustainable growth of the Japanese mechanical machinery manufacturing sector in 2007.

The first spinning machine made by this company was later developed in 1929, followed by the first rotor spinning machine (Open and End in 1968, and the first AirJet Loom Machine in 1980. This company has maintained its production of spinning and weaving machines up until this point by offering distinctive developments. By acquiring Oster Switzerland in 2012, the company has strengthened its foothold in the global textile market.
In 1933, Mr. Kiichiro Toyoda (the oldest son of Mr. Sakichi Toyoda) began producing automobiles in this business, which has been working as a standalone firm within the Toyota Group since 1937. The Toyota Industrial Group comprises the Toyota Motor Company and 12 other businesses. The group’s major shareholder is still Mr. Toyoda’s family.
In addition to leading the Toyota textile division, Mr. Tatsuro Toyoda, the grandson of Mr. Sakichi Toyoda, is currently president of the Japan Textile Machinery Association (JTMA).
TMT Machinery Company
This company’s name is an acronym for Toray Engineering, Murata Machinery, and Teijin Machinery, three of Japan’s largest machine manufacturing companies. Their machine manufacturing activity has been conducted since 2012, such as melt spinning, texturing, etc., for synthetic fiber manufacturing machinery. To gain a larger and more robust appearance on international markets and to avoid competition with one another, they are incorporated under the name TMT.
The Nishijin Jacquard Mfg. The company began producing jacquard loom machines in 1935 and renamed itself Murata Machinery in 1945. This company joined the spinning sector in 1946 by creating the first winder machines. In 1955, it could provide automatic cone winder machines thanks to a partnership with the American business Abbott.
It entered the melt-spinning sector in 1967 with the release of the first fi

lament yarn winder machines. Later that year, in 1967, it was also able to provide the first automatic texturing machines.
With the Air Jet Spinner (MJS) introduction in 1978, the company continued to make strides in weaving machines. Then, in 1997, it unveiled the Vortex Spinner (MVS), a cutting-edge spinning technology that uses compressed air vortexes and is in a special place in terms of the features of the finished yarn.
In 2002, Murata Company split its activities into spinning synthetic fibers. In collaboration with two other businesses, Toray Engineering and Tijin Siki Machinery, each functioning in this industry separately, it founded a new company named TMT.
In contrast to Murata Company, which continues to produce typical spinning machines, TMT Company is currently producing melt spinning machines, textile filament yarns (POY/FDY), industrial filament yarns, and texturing .
Along with running the Murata and TMT businesses, Mr. Daisuke Murata and Mr. Shosaku Miki serve as vice president and secretary of the Japan Textile Machinery Association, respectively.
Shima Seiki Co.
Masahiro Shima, a 1937-born man, launched his company in 1953 by inventing the first sewing machine. He created the initial semi-automatic glove knitting machine in 1960. This manufacturer later released the first flat knitting machine in 1967.
After that, this company’s flat knitting machine production became more serious. In 2015, following the release of dozens of innovative models, it eventually made the first computerized flat knitting machines capable of producing whole, seamless garments at the Itma Milan expo.
Mr. Masahiro Shima serves on the Japan Textile Machinery Association’s board of directors.

Birth of the world’s first WHOLEGARMENT computerized flat knitting machines
With the hollowing-out of industries due to the trend of globalization, we focused on domestic production and decided to develop the WHOLEGARMENT computerized flat knitting machines to convert the labour-intensive industry to a knowledge-intensive industry.
In 1995, the WHOLEGARMENT computerized flat knitting machines “SWG,” acclaimed as the “Oriental Magic,” knit a single sweater from yarn in only 30 minutes. This had a historical impact on the industry with an innovative solution of “eliminating sewing.”
In 1997, with the aim of creating products of “woven-like knitwear,” the “SlideNeedle” (needle for knitting), which was developed to enhance the appeal of WHOLEGARMENT, created its own knit fashion.
KANIA CO
In 1894, Mr. Komakichi Kana created a spinning traveler to launch his career. He continued his efforts by producing spinning needles in 1918. He expanded his business operations by making ring spinning in 1922 and card cover manufacture in 1973.
This company started making non-woven fabrics for particular purposes in 1949, and Mr. Hiroaki Kanai is currently in charge of this activity.
By acquiring the EADIE Company of England, one of the earliest known ring traveler manufacturers in the world (founded in 1871), in 1988, this company was able to grow its business markedly. To this day, it continues to produce ring travelers, ring, and card covers.

Scope of Business
- Manufacturing and sales of textile machinery parts
Manufacturing and sales of metal travellers, nylon travellers, single flange rings, porous sintered metal rings, metallic card clothing, top flats, worsted and woollen card clothing, raising fillet, and other kinds of Card clothing
- Manufacturing and sales of non-woven fabrics
Manufacturing and sales of materials for air conditioners, auto-related materials,
battery materials, basic materials for artificial, leather, construction materials, abrasives,
foundation materials, and other industrial materials
To create power looms for silk fabric production, Mr. Komajiro Tsuda began this company in 1909; it selected the name Tsudakoma in 1939. This business manufactured looms, dobbies, and twister machines in 1945. Additionally, he contributed to the manufacture of automatic looms, the development of shuttle looms, and the manufacture of warping sizers in 1951 and 1952, respectively.
The MAV Rapier Loom and the air and water jet Loom, the most significant devices this company offers, began manufacturing in 1968 and 1977, respectively.
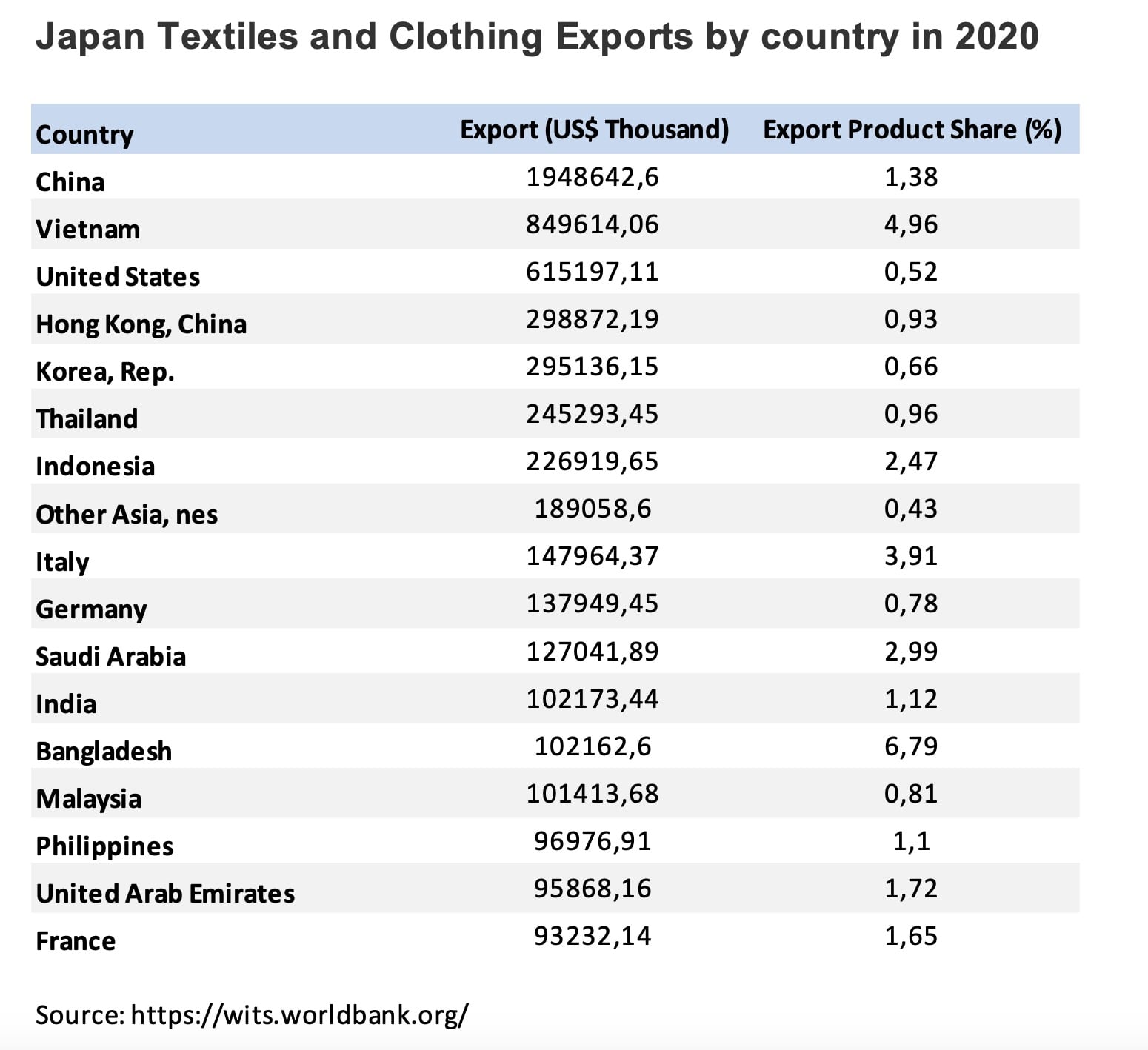
The leading exporters of textiles to Japan are China, Vietnam, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Cambodia, Italy, Thailand, Myanmar, Taiwan, and India.
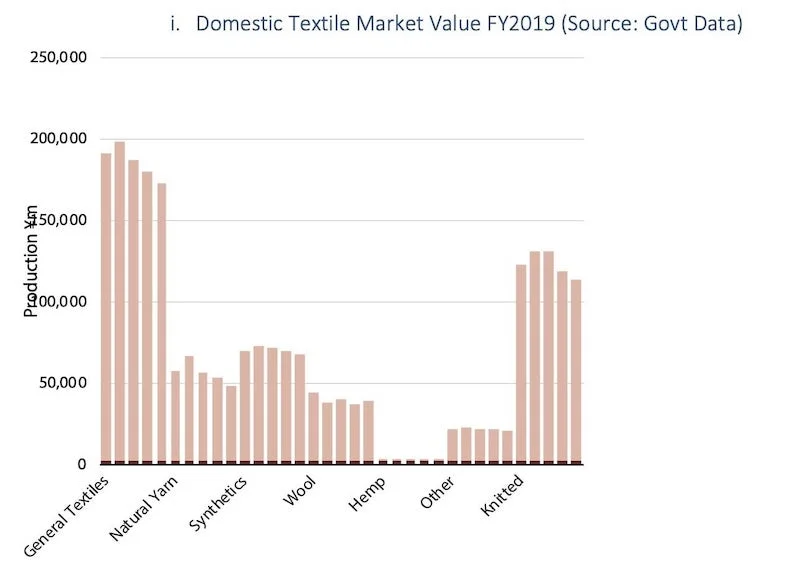
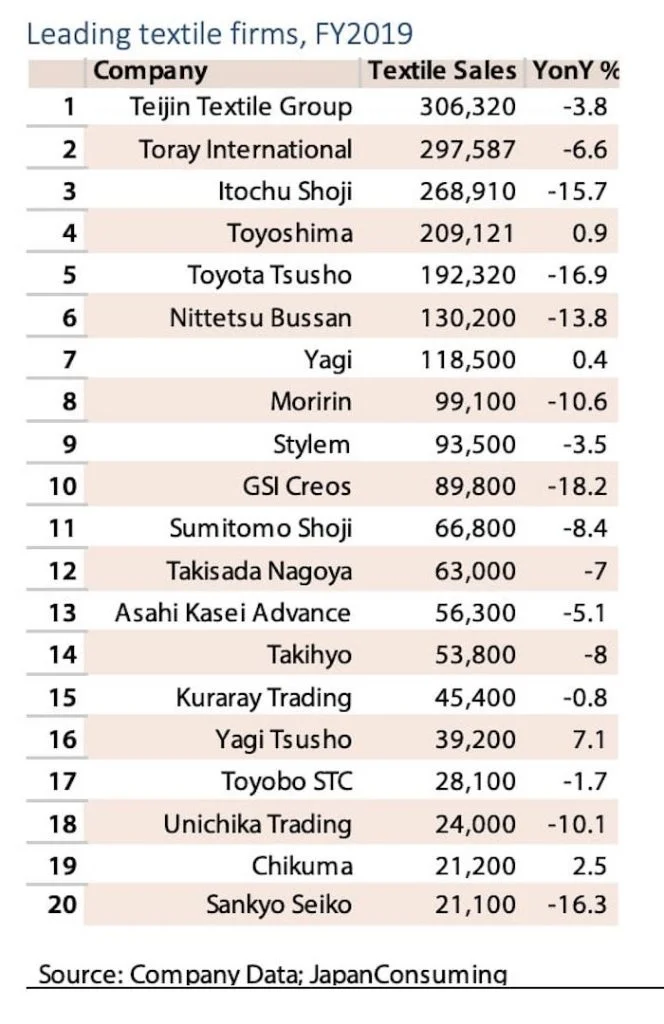
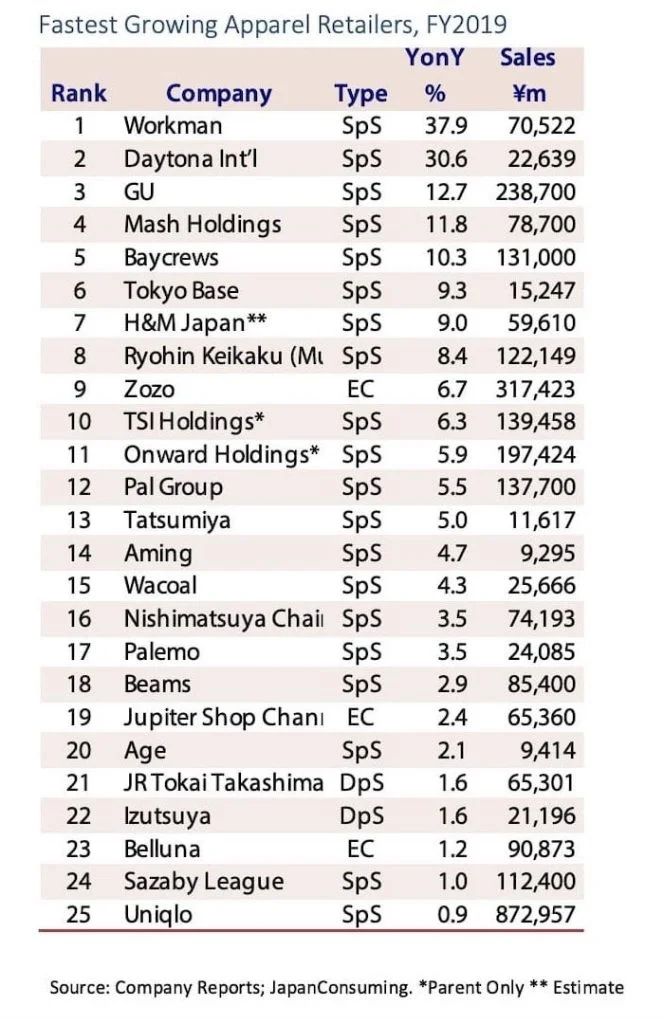
in below you can see some details and fact about Japan Textile and Apparel industry: